On January 11, 2023, James Webb’s Telescope again came to the attention of the media with its confirmation of the presence of an exoplanet, which was discovered back on August 13, 2022. NASA has confirmed that the size of the exoplanet is quite similar to that of Earth and has been named LHS 475b. The exoplanet LHS 475b is in the constellation Octans and situated 41 light-years away from Earth. For any telescope, exoplanets are difficult to spot due to the star’s bright light, around which they revolve. But by using the transiting observation method, James Webb’s Telescope, considered to be NASA’s most powerful and largest space science telescope, was able to find its first exoplanet. Continue reading to learn more about the telescope in depth and what it promises further.
James Webb Telescope
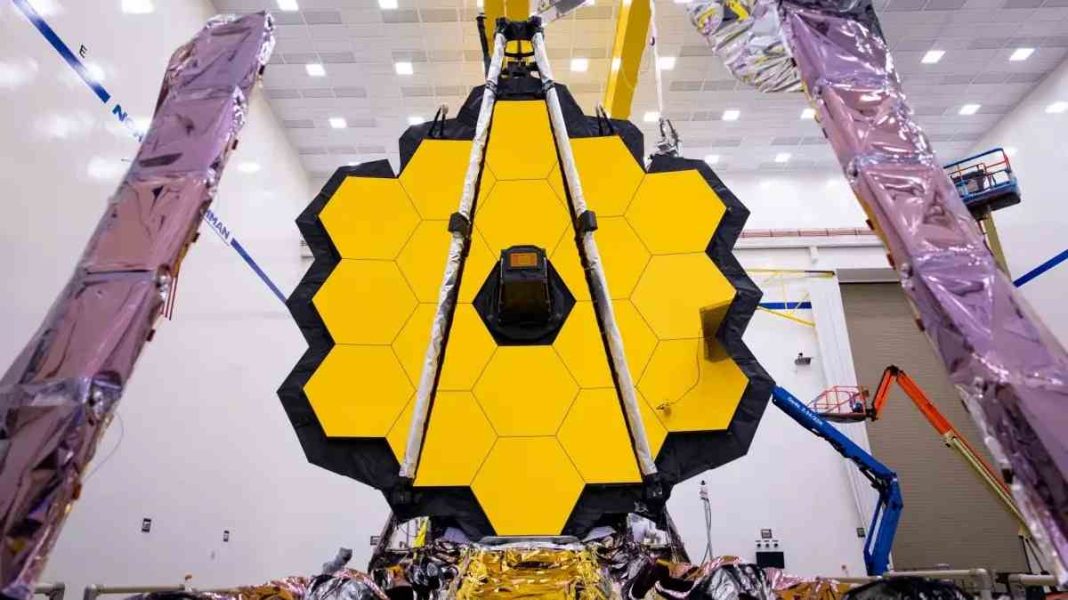
The James Webb Telescope (JWST) is the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and has the ability to conduct infrared astronomy. The space telescope will help to discover any cosmic events, habitable planets, and the coldest and most distant objects present in the universe. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), designed and developed the project.
Developmental History
Before the launch of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in 1990, the idea for another telescope to follow up on its findings was raised by NASA and the Space Telescope Science Institute. This idea for a space telescope that has the ability to study infrared astronomy materialized in the mid-1990s and was named the Next Generation Space Telescope, which would have a larger mirror than 13 ft.
In the next phase of things, industrial partners, academic experts, NASA centers, and international space agencies were roped into contributing to their testing facilities, building different parts for the telescope, and providing advice for the development and success of this project. The renaming of this project occurred in 2002 and was named after James Edwin Webb, who was the second administrator of NASA and also provided leadership to the agency during the Apollo program.
The construction of the James Webb Telescope (JWST) began in 2004; it was scheduled to launch in 2010, but the cost racked up to $10 billion, which was earlier estimated to be $1 billion. By 2011, the completion of the 18-segment primary mirror was achieved, and all the scientific instruments for the telescope were supplied to Goddard Space Flight Center by the end of 2015. NASA, along with the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), finished their cryogenic testing here. The flight components for the project were delivered in 2018 to Northrop Grumman Corporation, and in the same year, two halves of the Webb telescope were connected. From 2018 onwards, communication and environmental testing continued until 2021.
Launch And Location
The JWST was launched on December 25, 2021, from the Guiana Space Center at 12:20 p.m. GMT. The space center is located near Kourou in French Guinea, and the telescope was carried on the European Space Agency’s Ariana 5 rocket. The deployment of the full telescope occurred on January 8, 2022, and by January 24, the device had reached its final destination. The JSWT focused all its mirrors on a single star on March 16 for the first time, and NASA released the first scientific images taken by the device on July 12. The current location of the JWST is L2, which is a spot that lies opposite to the Sun yet close to the Earth. Like the HST, the JWST will not orbit the Earth; rather, it will orbit the Sun at a distance of 1.5 million kilometers from the Earth.
Specifications
The JWST approximately weighs 6200 kg, which is half that of the HST, and uses 2-kilowatt power. The primary mirror of the telescope has a diameter of 6.5 meters and has a gold coating on 18 separate hexagonal mirrors. The presence of a gold coating helps with infrared reflectivity, and the telescope has a collecting area of 25.4 meters square, which is six times more than HST. Red and orange visible light can also be seen through the telescope, though it is designed for infrared astronomy. For making correct observations, the temperature must be kept under 50 Kelvin, and the huge sun shield block present in the device protects it from heat and light from the earth, sun, and moon. For providing computing resources, electrical power, structural integrity, and cooling capability, the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) framework is used.
Goal Of The James Webb Telescope
Some of the long-term missions for the James Webb Telescope include:
Star Formation: Like all living beings, stars also have a life cycle where they are born and, with time, develop. And after a certain age, they die and provide raw materials for the formation of new stars. Though this process is well understood, until now no telescope could help make this formation visible due to the presence of a stream of dust around the new baby stars. With JWST’s infrared wavelength, the stream of dust would become translucent and make the formation visible.
Formation Of Galaxies: From the HST’s contribution of images, we now have a firm idea of what galaxies look like with their massive collections of stars aligned elegantly in different patterns. We have also come to know about the presence of black holes in the centers of most of these galaxies. Now, JWST probably will be able to answer certain questions, like how they were formed, how they combined, and many more such things.
Observing Other Worlds: Finding exoplanets similar to the Earth is one of the primary functions of JWST. By using its spectroscopy and infrared imaging, the telescope will be able to learn more about the physical and chemical properties of other planetary systems.
Conclusion
The discoveries made by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) have been astounding so far, and thus the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has quite a large shoe to fill. For the first few years, probably, the telescope will observe the most interesting things in the cosmic gamut. JWST has already discovered an exoplanet and provided some spectacular imagery of the world outside, and many scientists believe that it will become a household name like the HST.
See more: ‘ChatGPT’ Explained: Will ChatGPT End Google’s Relevance?